Transducer
A transducer is a device the technology of using instrument to measure and control the physical and chemical properties of materials is called instrumentation.This device convert energy from one to another to convert signal is called transducer. |
| Transducer |
Classification of transducers
Transducers are broadly classified into two groups as follows.
1. Active transducers.
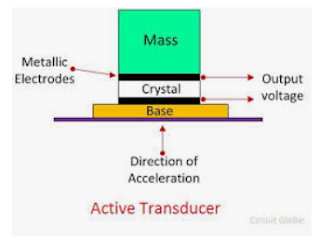
They are also known as self-generating type transducers. These transducers develop their own voltage or current. The energy required for production of an output signal is obtained from the physical phenomenon being measured.
Examples. Thermocouples and thermopiles, piezoelectric pick up, photo voltaic cell.
2. Passive transducers.
They are known as externally-powered transducers. These transducers device the power required for the energy conversion from an external, power source. However, they many absorb some energy from the physical phenomenon under study.
 |
| Passive transducer |
For example.
Resistance thermometer and thermistors, potentiometeric devices, differential transformer, photo-emission cell etc.
Resistance thermometer and thermistors, potentiometeric devices, differential transformer, photo-emission cell etc.
Classification based on type of output
1. Analogue transducer.
These transducer convert the input physical phenomenon into an analogues output which is a continuous function of time.
Example. Strain gauge, a thermocouple, a thermistor or an LVDT. Linear voltage differential transformer.
2. Digital transducers
These transducers convert the input physical phenomenon into an electrical output which may be in form of pulse.
3. Variable-capacitance type
4. Voltage-generating type
5. Voltage-generating type
Disadvantages
Thermistors are essentially semiconductors which behave as resistors with a high negative temperature co-efficient of resistance. The high sensitivity to temperature changes make the thermistors extremely useful for precision temperature -60 degree c. to +15 degree c. Measurements , control and compensation. Their resistance range from 0.5 ohm to 0.75 Mohm.
Thermistors are composed of sintered mixture of metallic oxides such as manganese, nickel, cobalt, copper, iron and uranium.
2. Digital transducers
These transducers convert the input physical phenomenon into an electrical output which may be in form of pulse.
Classification based on electrical principal involved
1. Variable-resistance type- Strain and pressure gauges
- thermistor, resistance thermometers
- photoconductive cell.
2. Variable-inductance type
- Linear variable differential transformer LVDT
- Reluctance pick-up.
- Eddy current gauge.
3. Variable-capacitance type
- Capacitor microphone
- pressure gauge
- Dielectric gauge
4. Voltage-generating type
- Thermocouple
- photovoltaic cell
- Rotational motion tachometer
- piezoelectric pick-up
5. Voltage-generating type
- Potentiometer position censor
- pressure-actuated voltage divider.
Electro-Mechanical Transducers
These days electrical/electronics of measurement are being increasingly applied to the measurement in many fields other than in electrical engineering. These methods claim the following advantages.
Advantage
- Less power consumption and less loading on the system to be measured.
- Friction and mass inertia effects minimum.
- More compact instrumentation.
- Possibility of non-contact measurement.
- Good frequency and transient response.
- Feasibility of remote indication and recording.
- Amplification greater than that produced by an mechanical contrivance.
- possibility of mathematical processing of signals like summation, integration etc.
Description of Transducers
Resistance transducers
In a resistance transducer an indication of measured physical quantity is given by a charge in the resistance. It may be classified as follows.
- Mechanically varied resistance -potentiometer
- Thermal resistance change -Resistance thermometers
- Resistivity change -Resistance strain gauge.
Linear and angular motion potentiometer
Such potentiometer convert the linear motion or the angular motion of a rotating shaft into changes in resistance. The device is a variable resistor whose resistance is varied by the movement of a slider over a resistance element.
- Translatory devices have strokes from 2.5 mm to 5 mm.
- Rotational devices have a full scale ranging from 10 degree to 60 degree full turn.
Advantage
- High output.
- Less expensive.
- Available in different sizes,shape and ranges.
- Rugged construction.
- Insensivity towards vibration and temperature.
- Limited life due to early wear of the sliding ram.
- The output tends to be noisy and erratic high speed operation or when used in high vibration environment.
Thermistors
These transducers are thermally sensitive variable resistors made of certain conducting and ceramic-like semiconducting materials. They are used as temperature detecting element used to sense temperature for the purpose of measurement and control. |
| Thermistor |
Thermistors are essentially semiconductors which behave as resistors with a high negative temperature co-efficient of resistance. The high sensitivity to temperature changes make the thermistors extremely useful for precision temperature -60 degree c. to +15 degree c. Measurements , control and compensation. Their resistance range from 0.5 ohm to 0.75 Mohm.
Thermistors are composed of sintered mixture of metallic oxides such as manganese, nickel, cobalt, copper, iron and uranium.
Application of thermistors
- Measurement of temperature .....major application.
- Temperature compensation in complex electronic equipment, magnetic amplifiers and instrumentation equipment.
- Measurement of power at high frequencies.
- Vacuum measurement.
- measurement of level, flow and pressure of liquids.
- Measurement of thermal conductivity.


wow nice article helped me a lot
ReplyDelete